

Georgy “The Voronator” Voronoy
This is a fast library for computing the [Voronoi diagram](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voronoi_diagram) of a set of two-dimensional points. It is based on [Delaunator](https://github.com/mapbox/delaunator), a fast library for computing the [Delaunay triangulation](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delaunay_triangulation) using [sweep algorithms](https://github.com/mapbox/delaunator/blob/master/README.md#papers). The Voronoi diagram is constructed by connecting the circumcenters of adjacent triangles in the Delaunay triangulation.
For an interactive explanation of how this library works, see [The Delaunay’s Dual](https://observablehq.com/@mbostock/the-delaunays-dual).
## Installing
If you use npm, `npm install d3-delaunay`. You can also download the [latest release on GitHub](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/releases/latest). For vanilla HTML in modern browsers, import d3-delaunay from Skypack:
```html
```
For legacy environments, you can load d3-delaunay’s UMD bundle from an npm-based CDN such as jsDelivr; a `d3` global is exported:
```html
```
## API Reference
### Delaunay
# new Delaunay(points) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the Delaunay triangulation for the given flat array [*x0*, *y0*, *x1*, *y1*, …] of *points*.
```js
const delaunay = new Delaunay(Float64Array.of(0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1));
```
# Delaunay.from(points[, fx[, fy[, that]]]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the Delaunay triangulation for the given array or iterable of *points*. If *fx* and *fy* are not specified, then *points* is assumed to be an array of two-element arrays of numbers: [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], …]. Otherwise, *fx* and *fy* are functions that are invoked for each element in the *points* array in order, and must return the respective *x*- and *y*-coordinate for each point. If *that* is specified, the functions *fx* and *fy* are invoked with *that* as *this*. (See [Array.from](https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/from) for reference.)
```js
const delaunay = Delaunay.from([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]);
```
# delaunay.points
The coordinates of the points as an array [*x0*, *y0*, *x1*, *y1*, …]. Typically, this is a Float64Array, however you can use any array-like type in the [constructor](#new_Delaunay).
# delaunay.halfedges
The halfedge indexes as an Int32Array [*j0*, *j1*, …]. For each index 0 ≤ *i* < *halfedges*.length, there is a halfedge from triangle vertex *j* = *halfedges*[*i*] to triangle vertex *i*. Equivalently, this means that triangle ⌊*i* / 3⌋ is adjacent to triangle ⌊*j* / 3⌋. If *j* is negative, then triangle ⌊*i* / 3⌋ is an exterior triangle on the [convex hull](#delaunay_hull). For example, to render the internal edges of the Delaunay triangulation:
```js
const {points, halfedges, triangles} = delaunay;
for (let i = 0, n = halfedges.length; i < n; ++i) {
const j = halfedges[i];
if (j < i) continue;
const ti = triangles[i];
const tj = triangles[j];
context.moveTo(points[ti * 2], points[ti * 2 + 1]);
context.lineTo(points[tj * 2], points[tj * 2 + 1]);
}
```
See also [*delaunay*.render](#delaunay_render).
# delaunay.hull
An Int32Array of point indexes that form the convex hull in counterclockwise order. If the points are collinear, returns them ordered.
See also [*delaunay*.renderHull](#delaunay_renderHull).
# delaunay.triangles
The triangle vertex indexes as an Uint32Array [*i0*, *j0*, *k0*, *i1*, *j1*, *k1*, …]. Each contiguous triplet of indexes *i*, *j*, *k* forms a counterclockwise triangle. The coordinates of the triangle’s points can be found by going through [*delaunay*.points](#delaunay_points). For example, to render triangle *i*:
```js
const {points, triangles} = delaunay;
const t0 = triangles[i * 3 + 0];
const t1 = triangles[i * 3 + 1];
const t2 = triangles[i * 3 + 2];
context.moveTo(points[t0 * 2], points[t0 * 2 + 1]);
context.lineTo(points[t1 * 2], points[t1 * 2 + 1]);
context.lineTo(points[t2 * 2], points[t2 * 2 + 1]);
context.closePath();
```
See also [*delaunay*.renderTriangle](#delaunay_renderTriangle).
# delaunay.inedges
The incoming halfedge indexes as a Int32Array [*e0*, *e1*, *e2*, …]. For each point *i*, *inedges*[*i*] is the halfedge index *e* of an incoming halfedge. For coincident points, the halfedge index is -1; for points on the convex hull, the incoming halfedge is on the convex hull; for other points, the choice of incoming halfedge is arbitrary. The *inedges* table can be used to traverse the Delaunay triangulation; see also [*delaunay*.neighbors](#delaunay_neighbors).
# delaunay.find(x, y[, i]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the index of the input point that is closest to the specified point ⟨*x*, *y*⟩. The search is started at the specified point *i*. If *i* is not specified, it defaults to zero.
# delaunay.neighbors(i) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns an iterable over the indexes of the neighboring points to the specified point *i*. The iterable is empty if *i* is a coincident point.
# delaunay.render([context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
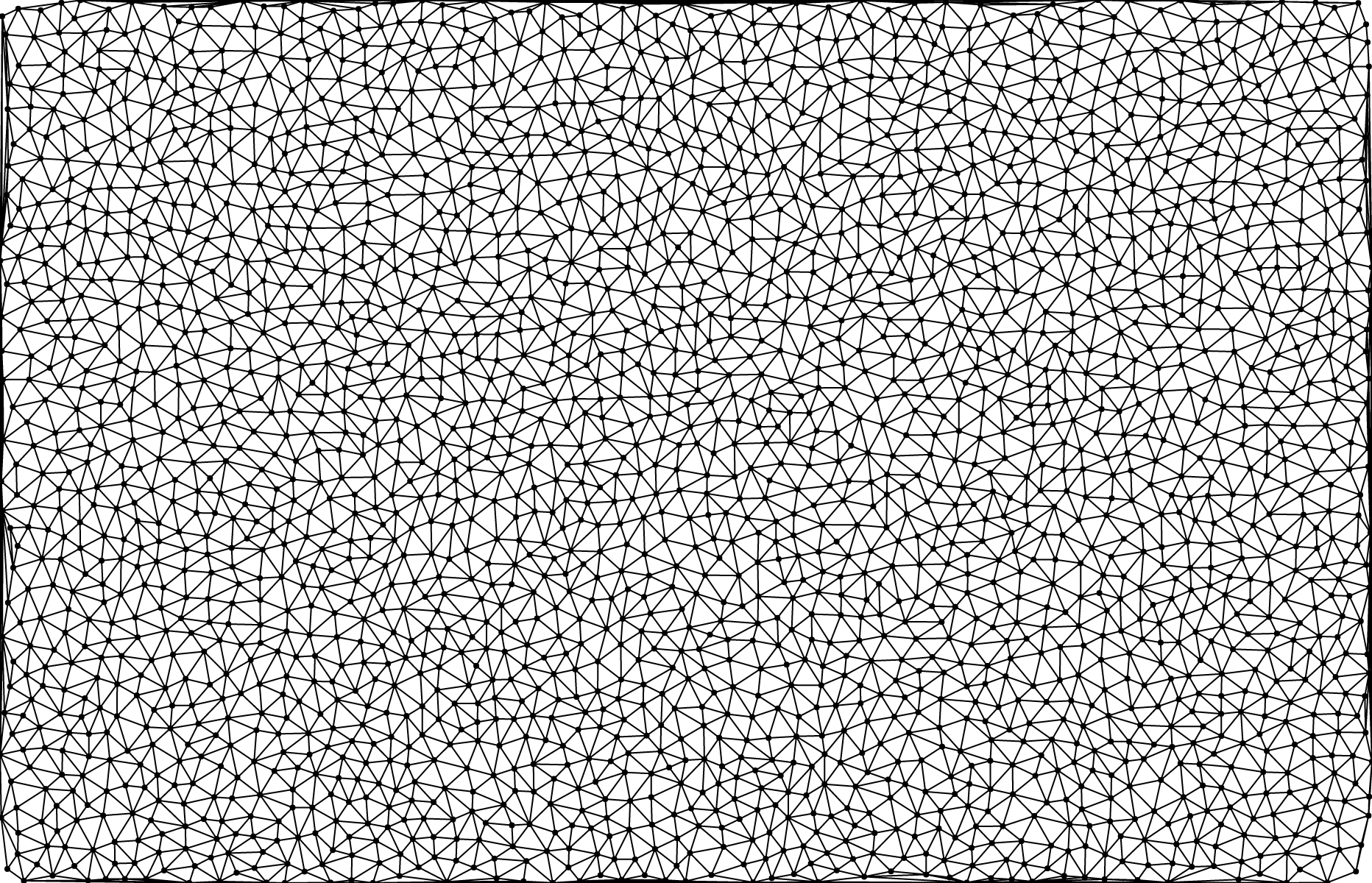 Renders the edges of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.lineTo methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.renderHull([context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Renders the edges of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.lineTo methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.renderHull([context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
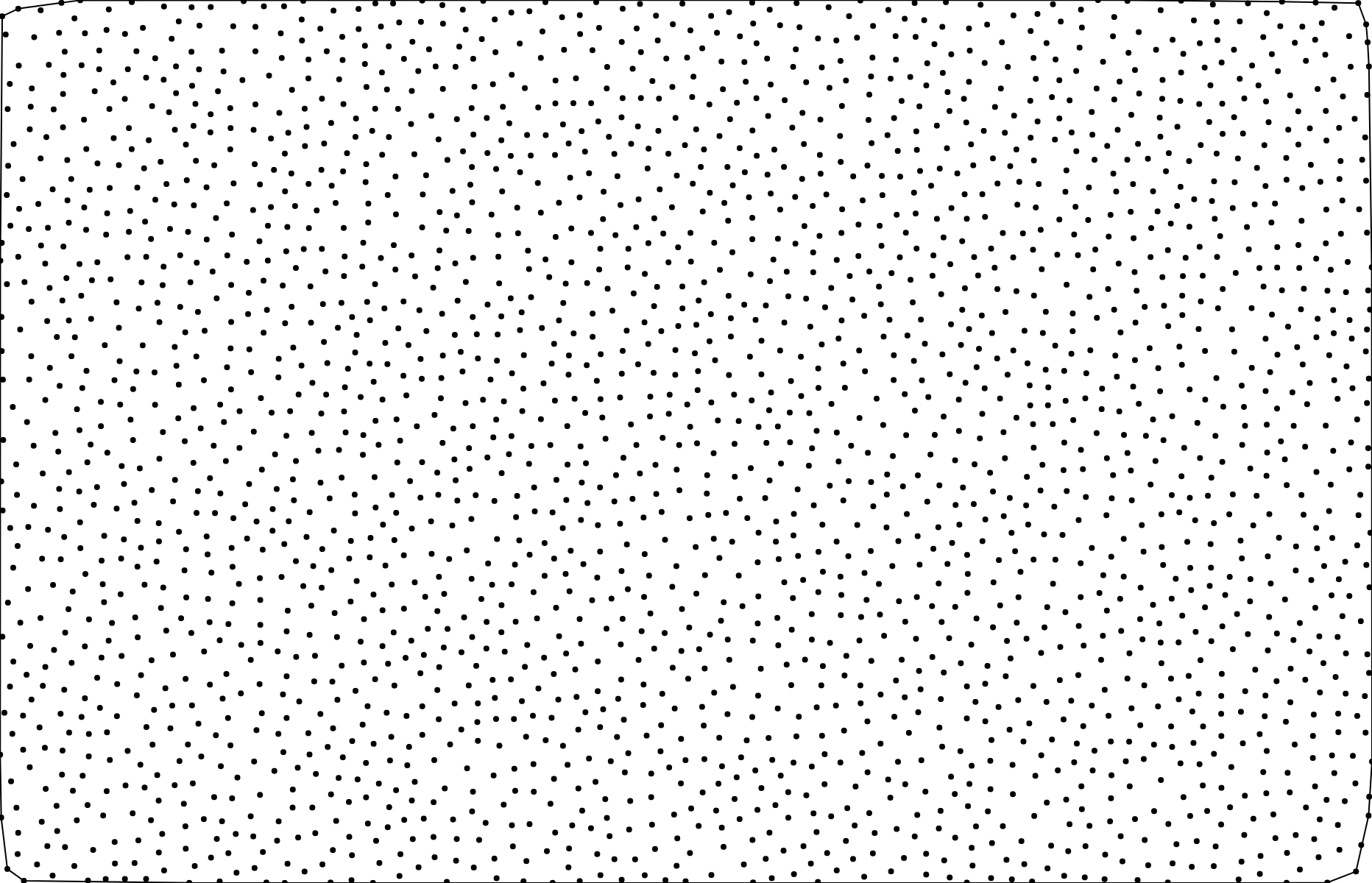 Renders the convex hull of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.lineTo methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.renderTriangle(i[, context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Renders the convex hull of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.lineTo methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.renderTriangle(i[, context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
 Renders triangle *i* of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo, *context*.lineTo and *context*.closePath methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.renderPoints(\[context\]\[, radius\]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Renders the input points of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context* as circles with the specified *radius*. If *radius* is not specified, it defaults to 2. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.arc methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.hullPolygon() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the closed polygon [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], …, [*x0*, *y0*]] representing the convex hull.
# delaunay.trianglePolygons() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns an iterable over the [polygons for each triangle](#delaunay_trianglePolygon), in order.
# delaunay.trianglePolygon(i) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the closed polygon [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], [*x2*, *y2*], [*x0*, *y0*]] representing the triangle *i*.
# delaunay.update() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Updates the triangulation after the points have been modified in-place.
# delaunay.voronoi([bounds]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the [Voronoi diagram](#voronoi) for the associated [points](#delaunay_points). When rendering, the diagram will be clipped to the specified *bounds* = [*xmin*, *ymin*, *xmax*, *ymax*]. If *bounds* is not specified, it defaults to [0, 0, 960, 500]. See [To Infinity and Back Again](https://observablehq.com/@mbostock/to-infinity-and-back-again) for an interactive explanation of Voronoi cell clipping.
The Voronoi diagram is returned even in degenerate cases where no triangulation exists — namely 0, 1 or 2 points, and collinear points.
### Voronoi
# voronoi.delaunay
The Voronoi diagram’s associated [Delaunay triangulation](#delaunay).
# voronoi.circumcenters
The [circumcenters](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Circumcenter.html) of the Delaunay triangles as a Float64Array [*cx0*, *cy0*, *cx1*, *cy1*, …]. Each contiguous pair of coordinates *cx*, *cy* is the circumcenter for the corresponding triangle. These circumcenters form the coordinates of the Voronoi cell polygons.
# voronoi.vectors
A Float64Array [*vx0*, *vy0*, *wx0*, *wy0*, …] where each non-zero quadruple describes an open (infinite) cell on the outer hull, giving the directions of two open half-lines.
# voronoi.xmin
Renders triangle *i* of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo, *context*.lineTo and *context*.closePath methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.renderPoints(\[context\]\[, radius\]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Renders the input points of the Delaunay triangulation to the specified *context* as circles with the specified *radius*. If *radius* is not specified, it defaults to 2. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.arc methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# delaunay.hullPolygon() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the closed polygon [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], …, [*x0*, *y0*]] representing the convex hull.
# delaunay.trianglePolygons() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns an iterable over the [polygons for each triangle](#delaunay_trianglePolygon), in order.
# delaunay.trianglePolygon(i) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the closed polygon [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], [*x2*, *y2*], [*x0*, *y0*]] representing the triangle *i*.
# delaunay.update() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Updates the triangulation after the points have been modified in-place.
# delaunay.voronoi([bounds]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/delaunay.js "Source")
Returns the [Voronoi diagram](#voronoi) for the associated [points](#delaunay_points). When rendering, the diagram will be clipped to the specified *bounds* = [*xmin*, *ymin*, *xmax*, *ymax*]. If *bounds* is not specified, it defaults to [0, 0, 960, 500]. See [To Infinity and Back Again](https://observablehq.com/@mbostock/to-infinity-and-back-again) for an interactive explanation of Voronoi cell clipping.
The Voronoi diagram is returned even in degenerate cases where no triangulation exists — namely 0, 1 or 2 points, and collinear points.
### Voronoi
# voronoi.delaunay
The Voronoi diagram’s associated [Delaunay triangulation](#delaunay).
# voronoi.circumcenters
The [circumcenters](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Circumcenter.html) of the Delaunay triangles as a Float64Array [*cx0*, *cy0*, *cx1*, *cy1*, …]. Each contiguous pair of coordinates *cx*, *cy* is the circumcenter for the corresponding triangle. These circumcenters form the coordinates of the Voronoi cell polygons.
# voronoi.vectors
A Float64Array [*vx0*, *vy0*, *wx0*, *wy0*, …] where each non-zero quadruple describes an open (infinite) cell on the outer hull, giving the directions of two open half-lines.
# voronoi.xmin
# voronoi.ymin
# voronoi.xmax
# voronoi.ymax
The bounds of the viewport [*xmin*, *ymin*, *xmax*, *ymax*] for rendering the Voronoi diagram. These values only affect the rendering methods ([*voronoi*.render](#voronoi_render), [*voronoi*.renderBounds](#voronoi_renderBounds), [*cell*.render](#cell_render)).
# voronoi.contains(i, x, y) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/cell.js "Source")
Returns true if the cell with the specified index *i* contains the specified point ⟨*x*, *y*⟩. (This method is not affected by the associated Voronoi diagram’s viewport [bounds](#voronoi_xmin).)
# voronoi.neighbors(i) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Returns an iterable over the indexes of the cells that share a common edge with the specified cell *i*. Voronoi neighbors are always neighbors on the Delaunay graph, but the converse is false when the common edge has been clipped out by the Voronoi diagram’s viewport.
# voronoi.render([context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
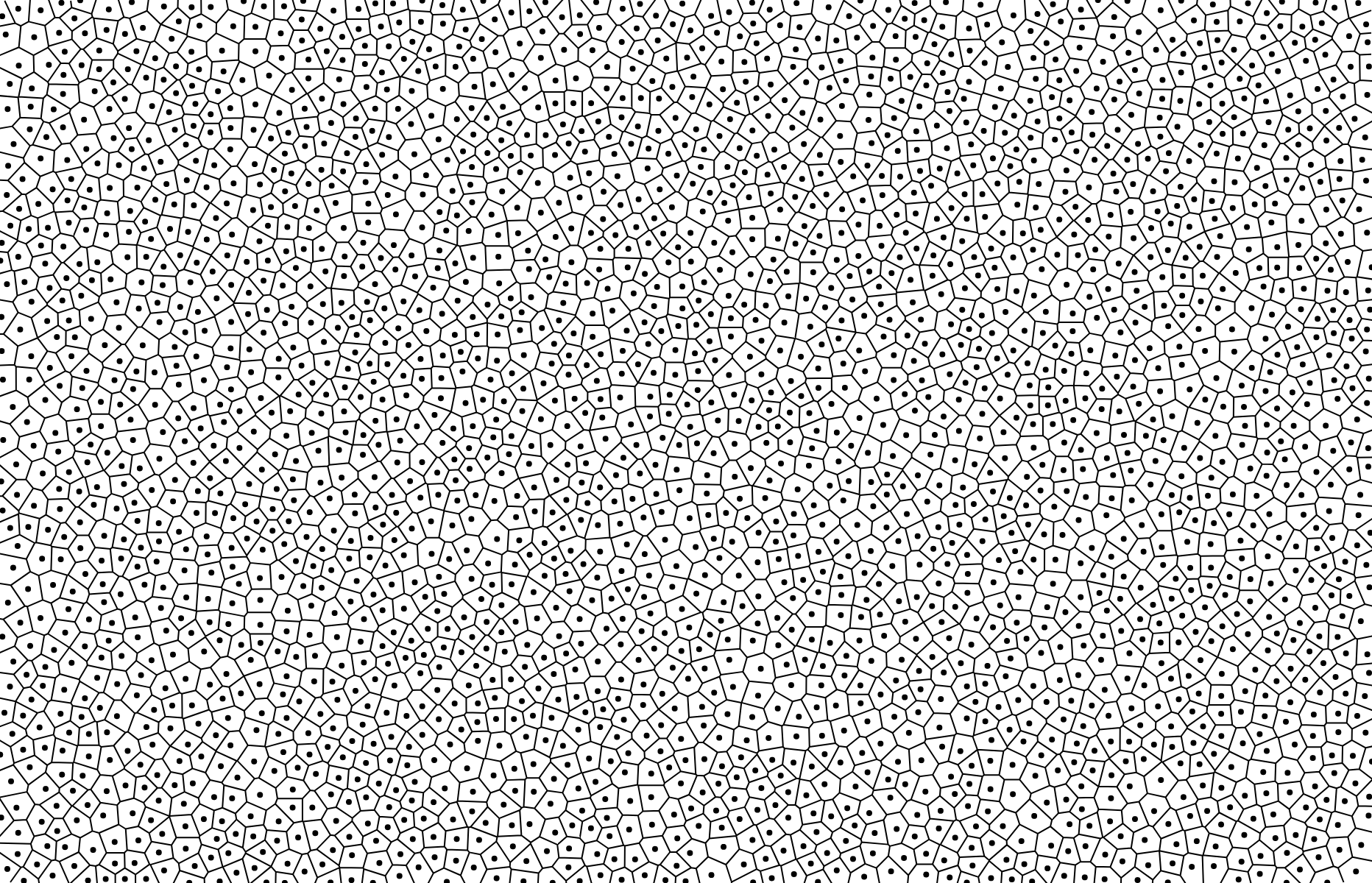 Renders the mesh of Voronoi cells to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.lineTo methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# voronoi.renderBounds([context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Renders the mesh of Voronoi cells to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo and *context*.lineTo methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# voronoi.renderBounds([context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
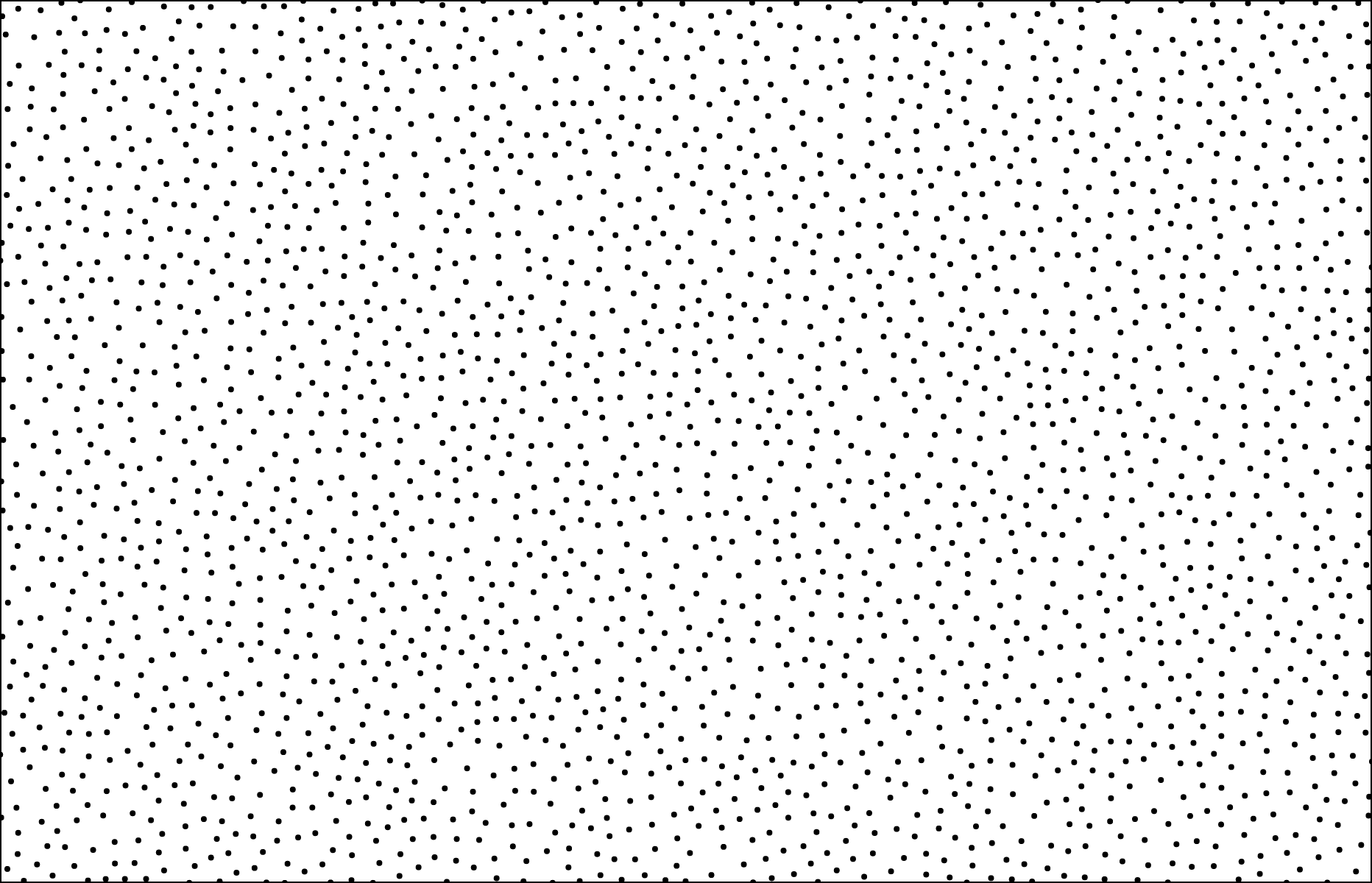 Renders the viewport extent to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.rect method from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). Equivalent to *context*.rect(*voronoi*.xmin, *voronoi*.ymin, *voronoi*.xmax - *voronoi*.xmin, *voronoi*.ymax - *voronoi*.ymin). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# voronoi.renderCell(i[, context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Renders the viewport extent to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.rect method from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). Equivalent to *context*.rect(*voronoi*.xmin, *voronoi*.ymin, *voronoi*.xmax - *voronoi*.xmin, *voronoi*.ymax - *voronoi*.ymin). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# voronoi.renderCell(i[, context]) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
 Renders the cell with the specified index *i* to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo , *context*.lineTo and *context*.closePath methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# voronoi.cellPolygons() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Returns an iterable over the non-empty [polygons for each cell](#voronoi_cellPolygon), with the cell index as property.
# voronoi.cellPolygon(i) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Returns the convex, closed polygon [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], …, [*x0*, *y0*]] representing the cell for the specified point *i*.
# voronoi.update() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Updates the Voronoi diagram and underlying triangulation after the points have been modified in-place — useful for Lloyd’s relaxation.
Renders the cell with the specified index *i* to the specified *context*. The specified *context* must implement the *context*.moveTo , *context*.lineTo and *context*.closePath methods from the [CanvasPathMethods API](https://www.w3.org/TR/2dcontext/#canvaspathmethods). If a *context* is not specified, an SVG path string is returned instead.
# voronoi.cellPolygons() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Returns an iterable over the non-empty [polygons for each cell](#voronoi_cellPolygon), with the cell index as property.
# voronoi.cellPolygon(i) [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Returns the convex, closed polygon [[*x0*, *y0*], [*x1*, *y1*], …, [*x0*, *y0*]] representing the cell for the specified point *i*.
# voronoi.update() [<>](https://github.com/d3/d3-delaunay/blob/master/src/voronoi.js "Source")
Updates the Voronoi diagram and underlying triangulation after the points have been modified in-place — useful for Lloyd’s relaxation.